Recommended Blogs
Why Cybersecurity Matters the Most in COVID-19 Pandemic?

Today, with the emergence of the latest Information Technology (IT), and its invasion to every aspect of life significantly defines its importance and dominance in real-world times. This very technological innovation has made the IT segment a potential target for cyber-attacks even during the pre-Covid-19 times.
- Glimpse of recent cybersecurity attacks in 2020
- Major Impacts for Businesses due to Cybersecurity Breaches
- Some of the cybersecurity threats amid Covid-19 pandemic are
- Cybersecurity Challenges for WFH employees during Covid-19
- Cybersecurity Challenges for Healthcare, Financial, Telecom, and E-learning Systems during Covid-19
- How can WFH employees and other Business Sectors overcome these Cyber Threats and Attacks?
- The need for businesses to leverage security testing to prevent cyber threats
- Conclusion
Remarkably, now as the world grapples with an unprecedented Covid-19 pandemic, the cyber-attackers and hackers are trying to take complete advantage of the rapid changes happening across various industries due to the ever-changing digital landscape, and thus, these cyber-attacks are becoming WFH employees: more rampant these days.
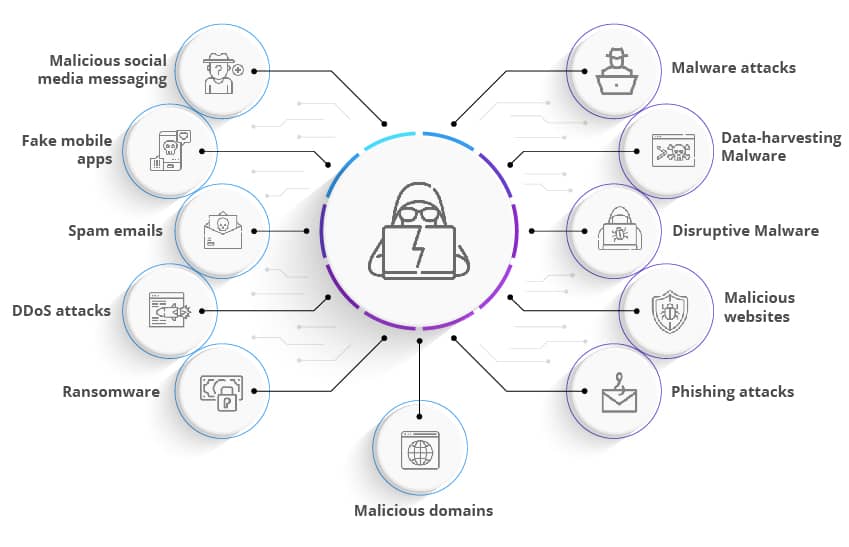
Invariably, the cyber-attackers are using this pandemic situation as a way of spreading malicious campaigns that include spam emails, malware, ransomware, banking malware, malicious websites, malicious domains, DDoS attacks, etc. The U.N. disarmament chief has warned that cybercrime is on the rise, with a 600% increase in malicious emails during the COVID-19 pandemic. The high representative for disarmament affairs said, growing digital dependency has increased the vulnerability to cyber-attacks, and it is estimated that one such attack takes place every 39 seconds.
Many organizations across the globe have encountered huge economic losses and even many brands had their businesses hit due to these rapidly growing cyber-attacks during these pandemic times, some of which have been detailed below.
Glimpse of recent cybersecurity attacks in 2020
◘ According to a Capgemini report, there has been a 667% increase in spear-fishing email attacks related due to COVID-19 since the end of February 2020 alone ◘ Another cybersecurity report states that the ransomware attacks are estimated to cost $6 trillion annually by 2021 ◘ According to Cybercrime Magazine, cybercrime is likely to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025 ◘ Twitter hackers who targeted Elon Musk and others, received $121,000 in Bitcoin in a recent cyber attack ◘ 67% of financial institutions reported an increase in cyber-attacks over the past year of 2019 ◘ The world’s largest cruise line operator reported a data breach due to a ransomware attack in August 2020 wherein hackers stole confidential information of customers, employees, and crew members ◘ 500,000 stolen Zoom passwords were available for sale in dark web crime forums ◘ Many healthcare organizations were struck by ransomware attacks and data breaches, stating that millions of their patient’s data were exposed ◘ 43% of cyber-attacks target small businesses
Let us also know some of the major impacts businesses face due to these cybersecurity breaches. Typically, each organization is unique in terms of the impact of the breach or cyber-attack which also depends on the timing and duration of the attack and also the industry involved. Specifically, if it is a financial industry the impact could be more rather than for manufacturing industry when these both industries are compared with respect to being affected due to these cyber attacks.
Major Impacts for Businesses due to Cybersecurity Breaches
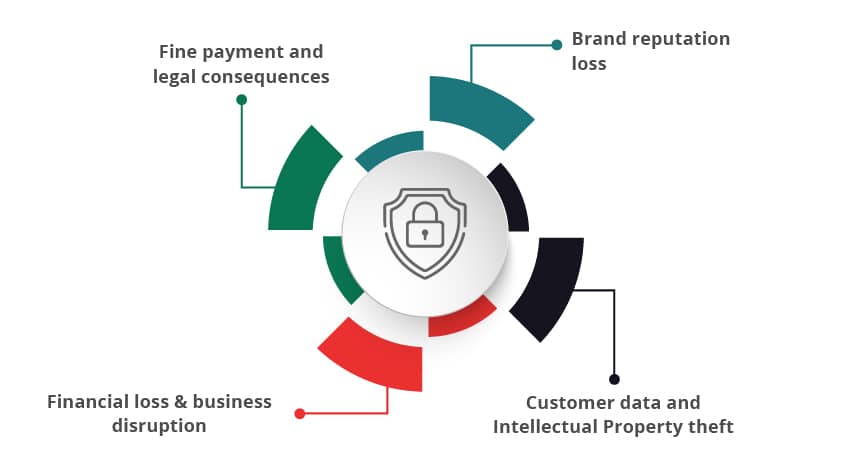
Brand reputation loss:
These cyber-attacks by hackers have caused some businesses to lose some of their customers and stakeholder’s trust, especially if the company has failed to protect their customer data. Invariably such a reputation loss might not attract the best talent, suppliers, or even investors, and might also lead to business disruption at times.
Customer data and Intellectual Property theft:
Continuous attacks by cybercriminals have led to monetary losses and especially this stolen data could be of more worth to the attackers. The stolen data is also sold on the dark web and hackers make good ransom these days. In addition, if Intellectual Property theft occurs, it might cause more harm to the companies as they lose their years of effort and R&D investment, due to these cybersecurity attacks.
Financial loss & business disruption:
Cybercrimes cause small businesses more damage when compared to large businesses or large corporations. According to a report, 43% of cyber-attacks are aimed at small businesses, but only 14% are prepared to defend themselves. Due to certain cyber-attacks, many of the leading corporate websites have gone down suffering many hours of business disruption in recent times.
Fine payment and legal consequences:
Businesses need to protect the personal data of customers or employees or patients, etc. If this data is accidentally or deliberately compromised, then it showcases that the organization has not followed appropriate security measures and they may be levied with fines and some might also have to face certain regulatory sanctions and legal consequences also.
Some of the cybersecurity threats amid Covid-19 pandemic are:
Cybersecurity Challenges for WFH employees during Covid-19
With the Work From Home (WFH) option still continuing for almost all corporate IT employees, their remote settings bring in more susceptibility to cybersecurity threats. The remote access, use of collaboration tools by employees, availability of enterprise data on endpoint devices, lack of physical oversight of IT infrastructure, continue to be some of the major grey areas for organizations and their WFH employees to be more susceptible to these cyber-attacks.
Cybersecurity Challenges for Healthcare, Financial, Telecom, and E-learning Systems during Covid-19
Healthcare systems:
Almost all modern-day healthcare systems are based upon ICT apps and these e-healthcare systems include e-pharmacy, telemedicine, virtual consultations using various apps, etc. In recent times, during this pandemic, these systems have become more vulnerable and have become more targeted systems for hackers.
Many of the healthcare systems across the globe have been attacked by various forms of cyber-attacks thus either causing business disruption or causing data theft of patient records.
Financial services:
For the financial sector, hacking and malware continue to be the primary cause of data breaches. 71% of all data breaches are financially motivated and typically the cost of cyberattacks in the banking industry reached $18.3 million annually per company, according to a recent report.
Alarmingly, 8 out of 10 US citizens fear that businesses are not able to secure their financial information and this financial report also states that 92% of ATMs are vulnerable to hacks. Thus, financial services organizations need to leverage effective measures and best security testing practices to safeguard customer data from possible threats.
Telecom systems:
According to a Deloitte report, telecom companies are a big target for cyber-attacks, as they build, control, and operate critical infrastructure that is being widely used to store large amounts of customer sensitive data. Cybercriminals or insiders are looking to blackmail customers, or even conduct identity theft, or launch furthermore attacks.
There are more risks involved even with the leased infrastructure equipment such as routers from Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and once it is compromised, then hackers use it to steal data, launch anonymous attacks, and many more which could lead to significant revenue loss to these telecom companies.
E-learning systems:
With schools closed for in person study, online learning environments have become the target for cyber attackers. The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) has warned that attackers could take advantage of COVID-19 by increasingly targeting virtual environments, including those utilized by school districts. The education sector has already been a prime target for ransomware attacks during these pandemic times. Another report from a leading Security firm said that many educational organizations are at risk of data security incidents during the current period of working from home and virtual learning on the go.
How can WFH employees and other Business Sectors overcome these Cyber Threats and Attacks?
Undoubtedly, cyber attackers have become smart in their moves and tactics but to defend systems from these attacks, businesses and organizations need to become even smarter by ensuring some best practices. Below mentioned are some of the best practices to adopt and protect their systems, applications and infrastructure from cyber-attacks.
Best practices to be followed:
Organizations should increase awareness among their employees, and educate them to identify potential risks, and stay away from any unsolicited emails, links, and messages, or malicious domains.
Both the employer and employees should ensure below mentioned best practices:
◘ Employees should be advised not to open up emails from unknown senders or from people who often do not communicate directly with them ◘ Employees should be advised not to click on links, or malicious domains if it comes from an unknown sender ◘ A corporate-approved anti-phishing filter or corporate-approved anti-virus must be installed by IT team to protect the company’s data from any possible cyber threats on each system ◘ Employees should maximize the usage of virtual private networks (VPNs), cloud interfaces, etc. to keep data safe and secure ◘ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) should be made necessary for all employees to access critical applications ◘ Password authentication should be followed and also ensure to keep their software updated
The need for businesses to leverage security testing to prevent cyber threats:
Organizations need to leverage security testing of their applications, systems, and infrastructure to safeguard them from any possible threats and vulnerabilities. Security testing is the key solution for preventing the organization’s apps, systems, and infrastructure from cyber-threats and vulnerabilities. Security testing is a rigorous testing process performed by using various open-source and commercial automation security testing tools to help identify any weaknesses, or vulnerabilities in the systems, applications, or networks.
The security testing process consists of security scanning, vulnerability scanning, security review, security auditing, penetration testing, etc. The ultimate objective of security testing is to identify vulnerabilities and threats in the organization and to properly safeguard systems.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, cybersecurity is an uprising issue, especially during these unprecedented pandemic times. Many businesses have turned towards digital solutions to ensure the longevity of their businesses. But, inevitably, with the usage of these digital solutions, many organizations are more prone to cybersecurity attacks. Hence, brands must leverage effective security testing services from next-gen security testing services provider to safeguard their systems, apps, data, and IT infrastructure from cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
How can TestingXperts help in preventing your organization from cyber-attacks?
We have a team of Certified Ethical Hackers (CEH) who can help you to ensure that your application is secure from any vulnerabilities and that it meets the essential security requirements like confidentiality, authorization, authentication, availability, and integrity.
We are one of the best security testing companies that have expertise in assessing a wide range of applications for security threats and we ensure that your application is rigorously tested for all possible threats and vulnerabilities. We also perform vulnerability testing and pen testing to safeguard your systems, apps, and infrastructure from any possible security threats.
We primarily follow the OWASP (Open Web Security Project) guidelines in our security testing services along with PCI-DSS, HIPAA, SOX, WAHH, OSSTM, WASC, and NIST Standards as per the application-specific requirements.
FAQs
Here are four major impacts due to cybersecurity breaches.
1. Brand reputation loss
2. Customer data and Intellectual Property theft
3. Financial loss & business disruption
4. Fine payment and legal consequences
Undoubtedly, cyber attackers have become smart in their moves and tactics but to defend systems from these attacks, businesses and organizations need to become even smarter by ensuring some best practices. Below mentioned are some of the best practices to adopt and protect their systems, applications and infrastructure from cyber-attacks.
We have a team of Certified Ethical Hackers (CEH) who can help you to ensure that your application is secure from any vulnerabilities and that it meets the essential security requirements like confidentiality, authorization, authentication, availability, and integrity.
Discover more
