Recommended Blogs

A Beginner’s Guide to Test Automation 2026
Table of Content
- What is Automation Testing?
- What Does Test Automation Do?
- Significance of Automation in Testing for Enterprises?
- Best Practices of Test Automation
- Benefits of Automation Testing
- What Are the Types of Automation Testing?
- Some of the Most commonly Used Test Automation Tools Are:
- How Does Test Automation Works?
- Business Benefits with a well-defined Test Automation Approach
- How Is AI Integrated into Test Automation Frameworks?
- Cloud-Based Test Automation for Scalability
- What Does an Automation Tester Do?
- What Are Automation Testing Challenges and How to Overcome Them?
- Automation Testing Vs Unit Testing
- Why Should You Leverage Next-gen Testing Services Provider for Test Automation?
As software development continues to accelerate in 2026, the demand for high-quality applications delivered rapidly and reliably has never been greater. Test automation has become an indispensable part of this journey, enabling teams to execute repetitive tests efficiently, improve test coverage, and accelerate release cycles. For beginners, understanding the fundamental concepts, tools, frameworks, and best practices of test automation is essential to building a strong foundation and contributing effectively to modern software quality assurance.
This guide is designed to introduce newcomers to the evolving landscape of test automation in 2026, covering why automation matters, how to get started, key tools and frameworks to know, and practical tips for successful implementation. Whether you are a QA professional, developer, or stakeholder new to automation, this beginner-friendly resource will help you navigate the essentials and set you on the path to mastering automated testing.
What is Automation Testing?
Test automation broadly involves running scripts executed through specialized software testing tools to automate test case execution and result verification. It ensures high accuracy and reliability since there is no human intervention, thereby reducing errors that often occur in manual testing. Automation testing is especially suited for repetitive and critical testing types such as regression, performance, load, and security testing. By leveraging both open-source and commercial tools, automation efficiently handles large test suites, increases test coverage, speeds up feedback loops, and supports continuous integration and delivery processes. This results in faster, more consistent, and cost-effective software quality assurance overall.
What Does Test Automation Do?
Test automation broadly involves running scripts executed through specialized software testing tools to automate test case execution and result verification. It ensures high accuracy and reliability since there is no human intervention, thereby reducing errors that often occur in manual testing. Automation testing is especially suited for repetitive and critical testing types such as regression, performance, load, and security testing. By leveraging both open-source and commercial tools, automation efficiently handles large test suites, increases test coverage, speeds up feedback loops, and supports continuous integration and delivery processes. This results in faster, more consistent, and cost-effective software quality assurance overall.
Significance of Automation in Testing for Enterprises?
The significance of automation in testing for enterprises in 2026 is profound and multifaceted:
- Faster and More Frequent Feedback: Automation enables rapid test execution and immediate feedback during development, which accelerates validation at various phases of product development. This is crucial for enterprises aiming for faster releases without compromising quality.
- Reduced Manual Intervention and Enhanced Reliability: Automated test scripts run with minimal human interference, reducing human error and increasing the reliability and accuracy of test results compared to manual testing. This consistency ensures defects are detected promptly and precisely.
- Improved Collaboration Across Teams: Automated testing facilitates better communication and collaboration between DevOps, QA, and product management teams by providing trustworthy, real-time test results that stakeholders depend on for decision-making.
- Scalability for Multiple Versions and Platforms: For enterprises supporting applications across numerous versions, operating systems, devices, and platforms, automation offers the repeatability and scalability needed to run extensive test suites efficiently.
- Suitability for Regression and High-Risk Testing: Automation is especially well-suited for regression tests and testing critical functionalities repeatedly, ensuring that new changes do not break existing features under real-time conditions.
- Cost Savings and Risk Mitigation: Although initial automation setup requires investment, it ultimately saves costs by preventing software failures, reducing testing time, and minimizing defects reaching production, which can cause significant business losses.
- Supports Agile and DevOps Practices: Automation aligns with modern software development workflows like Agile and DevOps, supporting continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, thus enabling faster, reliable, and high-quality software releases.
- Efficient Use of Resources: By automating repetitive testing tasks, QA teams can focus on exploratory testing and other strategic activities, thereby optimizing resource allocation and productivity.
In essence, automation testing empowers enterprises to deliver high-quality software at speed and scale, increasing confidence in software stability while reducing time-to-market and overall testing costs. This makes test automation a critical pillar in enterprise software quality strategies in 2026
Best Practices of Test Automation
Select the Right Automation Tool
Choose automation tools that align with your project’s technology stack, testing needs, and team expertise. The right tool will maximize efficiency and ensure smooth execution of automated tests.
Design Tests Before Automating Them
Create well-structured test cases before automation begins. Good test design is fundamental for identifying defects early and ensuring thorough coverage, building a strong foundation for automation scripts.
Don’t Plan to Automate Unstable Functionality
Avoid automating features or components that are still changing. Focus automation efforts on stable functionalities, as automating unstable code leads to frequent script breakages and unnecessary maintenance.
Decide Which Tests to Automate
Not all test scenarios are suitable for automation. Prioritize automating repetitive, high-impact, and critical test cases, while leaving complex exploratory and usability checks for manual testing. A thoughtful automation strategy balances coverage and efficiency.
Early and Frequent Testing
Integrate automated testing early in the development lifecycle and run tests frequently—ideally with every build or code change. This enables rapid detection and resolution of defects, saving significant time and costs compared to catching bugs later.
Do Not Completely Rely on UI Test Automation
While UI tests are important, they can be fragile due to frequent interface changes. Complement UI automation with API, integration, and unit tests to achieve more robust and reliable overall test coverage.
Summary: Applying these best practices improves automation ROI by boosting efficiency, reducing maintenance, and accelerating time-to-market—ultimately contributing to higher-quality software releases.
Benefits of Automation Testing
There are many benefits with Test Automation which have been broadly classified as Qualitative and Quantitative benefits.
Qualitative Benefits of Automation in Testing
- Accelerates Testing Cycles: Automated test runs drastically speed up the testing process, making it possible to validate software more frequently and efficiently.
- Reduces Test Execution Time: Automation executes tests much faster than manual efforts, especially for large or repetitive test suites.
- Increases Test Coverage: Enables comprehensive testing across more scenarios, platforms, and configurations with each cycle.
- Simplifies Test Case Maintenance: Modern frameworks make it easier to update and maintain test cases as applications evolve.
- Minimizes Script Updates: Well-designed automation frameworks reduce the effort needed to update scripts, even as application features change.
- Speeds Up Script Generation: Automated tools streamline the creation of test scripts, enabling rapid scaling of test coverage.
- Enhances Code Reusability: Automation frameworks promote modularity, allowing code and test components to be reused across different scenarios and projects.
- Reduces Manual Effort: Automation handles repetitive tasks, freeing up QA teams to focus on functional, exploratory, and user-experience testing.
- Shortens Testing Timelines: Automated workflows dramatically compress overall testing schedules.
- Optimizes Regression Testing: Automation is especially effective for regression testing, rerunning large suites quickly to catch new defects.
- Improves Accuracy: Automated tests eliminate human error, delivering more consistent and reliable test results.
- Modularizes Complex Processes: Large business processes can be split into reusable, manageable components, improving flexibility and efficiency.
- Extends Automation Code Life: Well-structured automation scripts have longer lifespans and require less frequent rewrites.
- Boosts Team Productivity: By increasing testing speed, teams can deliver quality software more rapidly.
What Are the Types of Automation Testing?
Automation testing encompasses various approaches designed to validate different aspects of software efficiently and accurately. Each type targets a specific layer or functionality within the application, helping teams ensure comprehensive quality assurance across the development lifecycle. Selecting the right mix of automation testing types is key to detecting defects early, maintaining stability, and supporting rapid, reliable software releases.
Unit Testing:
The earliest stage of automation testing, focusing on individual components or units of code. Typically written by developers (and sometimes testers), unit tests verify that each function or method performs as intended. These are conducted during software development to catch defects early.
Smoke Testing:
Also called “build verification testing,” smoke testing checks whether a software build is stable enough for further testing. Only key functionalities are tested; unstable builds are rejected and sent back to developers, while stable builds move forward in the QA process.
Black Box Testing:
In this approach, testers assess the application’s external behavior without knowing its internal code structure. Black box tests are designed to identify missing or incorrect functions, interface and performance errors, behavioral anomalies, and termination errors.
Integration Testing:
This type validates the interactions and data communication between integrated modules or services of an application. Once individual units are confirmed to work, integration tests assess their ability to function correctly together.
Functional Testing:
Functional testing ensures that all application features work according to the requirements. It includes API testing, database verification, security testing, and checks the system’s overall functionality from an end-user perspective.
Regression Testing:
After changes or updates to the codebase, regression testing verifies that existing functionalities remain unaffected. This comprehensive approach ensures that enhancements or bug fixes have not introduced new issues or disrupted previous features.
Summary: Each type of automation testing plays a unique role in ensuring software quality—spanning code-level validation to system-wide checks—enabling early detection of defects and supporting faster, more reliable releases.
Some of the Most commonly Used Test Automation Tools Are:
Selecting the right test automation tool is crucial for achieving efficient, scalable, and reliable automated testing. Today’s market offers a mix of open-source and commercial solutions, each catering to different platforms, application types, and testing requirements. Understanding the strengths and unique features of these popular tools can help teams choose the best fit for their projects and streamline their software quality assurance process.
Selenium:
A leading open-source tool for web automation testing, highly favored in DevOps environments. Selenium consists of two main components: WebDriver, which automates browsers for end-to-end testing, and Selenium IDE, which provides a simple user interface for recording and playing back tests. Selenium is flexible, supports multiple programming languages, and is backed by a strong community—making it a top choice for automating web applications.
Appium:
An open-source automation framework tailored for testing native, hybrid, and mobile web applications on both Android and iOS platforms. Appium allows testers to use their preferred programming languages and frameworks, supports cross-platform testing, and is ideal for mobile app automation across devices and OS versions.
Cucumber:
An open-source tool focused on Behavior-Driven Development (BDD). Cucumber allows collaboration between technical and non-technical stakeholders by using plain-text specifications (written in Gherkin syntax) that double as executable test scripts. It is widely used for automating acceptance tests and ensuring that development aligns closely with business requirements.
Ranorex:
A robust automation tool for web, desktop, and mobile applications. Ranorex stands out for its user-friendly interface, strong object recognition, and support for both coded and codeless automation. It’s suitable for teams seeking a comprehensive solution for cross-platform testing without steep learning curves.
TestComplete:
An advanced automation tool notable for its AI-powered visual recognition engine, allowing both script-based and scriptless test creation. TestComplete supports automation for desktop, web, and mobile apps and lets users work with various scripting languages or leverage its intuitive record-and-playback features.
Micro Focus UFT (Unified Functional Testing):
A widely used enterprise tool for regression, functional, API, and web services testing. UFT excels at automating tests for complex business applications, including ERP and CRM solutions, and integrates easily with continuous testing pipelines.
Apache JMeter:
An open-source performance testing tool built in Java, famous for its ability to simulate heavy loads on web applications and analyze performance. JMeter’s capabilities extend to functional testing and support for a variety of protocols, making it indispensable for measuring application scalability and robustness.
Tosca:
An enterprise-grade test automation tool known for its model-based approach, allowing rapid creation and maintenance of test cases. Tosca supports end-to-end functional, load, and risk-based testing, as well as test data management and automation across modern app architectures.
These tools cover a spectrum of automation needs, from UI/web testing and mobile automation to API, performance, and full enterprise application testing. The right tool depends on your project’s technology stack, automation goals, team skill sets, and specific testing requirements.
How Does Test Automation Works?
Test automation involves using specialized tools and scripts to automatically execute predefined test cases, validate software behavior, and compare actual results with expected outcomes. This process reduces manual intervention, increases accuracy, and accelerates feedback during development. Automated testing is integrated into the software lifecycle—especially in modern Agile and DevOps workflows—where tests are repeatedly run to ensure code changes don’t introduce new defects.
10 Basic Steps for a Well-Defined Test Automation Process:
- Evaluate the Need for Automation: Assess whether automation adds value to your project based on the application type, complexity, and frequency of changes.
- Define Automation Goals and Priorities: Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with automation—such as reducing regression cycles, improving coverage, or speeding up releases.
- Plan Automated Testing Strategy: Develop a roadmap detailing scope, approach, team roles, and how automation will fit within your overall test process.
- Select the Right Automation Tool & Framework: Choose tools and frameworks that match your technology stack, application type, and team expertise.
- Decide What Test Cases to Automate: Identify redundant, stable, high-impact, or time-consuming test cases that offer the highest return when automated.
- Develop Good Quality Test Data: Create or source diverse, realistic, and reusable test data to ensure tests reflect real-world scenarios and edge cases.
- Create Automated Tests Resistant to UI Changes: Design modular, maintainable, and robust scripts (using techniques like the Page Object Model) to minimize script failures due to UI updates.
- Execute Tests for Developed Scripts: Run automated test suites regularly to validate application behavior and catch new defects early.
- Test Early and Often with CI/CD Patterns: Integrate automation into your continuous integration/continuous delivery pipeline so tests are triggered automatically on every code change.
- Maintain the Test Scripts: Regularly review, update, and refactor automation scripts to align with evolving application functionality and keep your test suite effective and reliable.
By following these steps, teams can structure their automation efforts for maximum efficiency, scalability, and long-term value, ensuring reliable and continuous software quality throughout the development lifecycle.
Business Benefits with a well-defined Test Automation Approach
- Delivers quality software products
- Increases release velocity through the CI/CD model
- Reduces human errors as human tasks are automated
- Ensures cost optimization
- Maximizes ROI
- Ensures faster time to market
How Is AI Integrated into Test Automation Frameworks?
AI in test automation is changing automation from running scripts to adaptive testing. AI-powered frameworks learn how applications work overtime, so they don’t break when locators or flows change. They examine past runs, failures, and code changes to improve the code’s performance in the future. Where AI really helps:
- Test scripts that fix themselves when the UI changes
- Choosing tests based on risk and past failures
- Visual validation to find UI regressions that go beyond DOM checks
- Finding flaky or unstable tests early on
Teams spend less time debugging scripts and more time making sure that essential business functions work.
Cloud-Based Test Automation for Scalability
Cloud test automation takes away the need for infrastructure.
Teams can dynamically scale test runs by running tests in the cloud, rather than relying on fixed setups on their own premises. This is especially useful for businesses that frequently release new versions of their software on multiple platforms.
Some significant results of cloud test automation are:
- Running at the same time on different browsers, devices, and OS versions
- Faster regression cycles with no problems in the environment
- Lower operational costs using usage-based models
- Teams that work together around the world can do so more easily.
Cloud test automation ensures that the amount of testing that can be done increases at the same rate as the speed of development.
What Does an Automation Tester Do?
An automation tester, also known as a QA automation tester or automation test engineer, is responsible for driving the test automation process to ensure the timely and successful delivery of high-quality software products.
Here’s what their role typically involves:
- Designing and Writing Automation Scripts: The automation tester creates detailed test automation scripts tailored to the application under test. These scripts are based on predefined requirements and use various automation frameworks suited for the project.
- Utilizing Test Automation Frameworks: Automation testers work with different test automation frameworks (such as Selenium, Appium, TestComplete, and more) to structure and standardize their automated test cases, supporting efficient, maintainable, and scalable test automation initiatives.
- Executing Automated Test Scenarios: They run automated test scripts to validate that all defined scenarios—functional and non-functional—are appropriately covered. This ensures that new features and existing functionalities are working as intended.
- Collaboration and Issue Logging: Automation testers work closely with developers, manual testers, and other QA team members. When defects or issues are identified during automated test runs, they document and log these bugs in test management or defect tracking tools, enabling developers to quickly address them.
- Performing Regression Testing: After developers resolve reported bugs and introduce new features, automation testers re-execute automated regression test suites. This step confirms that recent code changes do not negatively impact the stability or performance of existing features.
- Continuous Process Improvement: They contribute to ongoing improvements by updating test scripts, refining test coverage, and optimizing automation practices to align with evolving project needs and business goals.
In summary, automation testers play a crucial role in accelerating the testing process, improving software quality, and supporting rapid, reliable software releases by leveraging automation tools, scripting expertise, and cross-functional collaboration.
What Are Automation Testing Challenges and How to Overcome Them?
Automation testing offers significant advantages, but its success can be hindered by several key challenges. Below is a detailed overview of major automation testing challenges and proven strategies to overcome them:
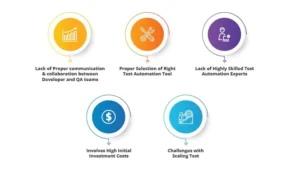
1. Lack of Communication & Collaboration Between Developer and QA Teams
Challenge: Poor communication and collaboration among developers, QA engineers, and operations teams can stall automation initiatives and cause misunderstandings about requirements and objectives.
How to Overcome:
- Foster a Collaborative Culture: Ensure cross-functional teams are involved from the outset—defining clear test automation goals together.
- Regular Meetings and Transparent Processes: Hold frequent discussions (stand-ups, retrospectives) and use collaborative tools (like Jira, Slack, Confluence) to maintain clarity on roles, requirements, and progress.
- Shared Documentation: Maintain well-documented requirements, test cases, and automation strategies accessible to all stakeholders.
2. Proper Selection of the Right Test Automation Tool
Challenge: Selecting a tool misaligned with the application’s requirements can result in compatibility issues, inadequate coverage, or excessive costs.
How to Overcome:
- Thorough Evaluation: Involve QA automation experts in evaluating both open-source and commercial tools, focusing on compatibility with the application under test (AUT), technology stack, and project roadmap.
- Proof of Concept (PoC): Pilot shortlisted tools on representative test cases before full-scale adoption.
- Consider Scalability and Integration: Choose tools that integrate well with your CI/CD pipeline and can scale as your application grows.
3. Shortage of Highly Skilled Test Automation Experts
Challenge: A lack of skilled automation engineers can lead to poor framework design, fragile test scripts, and maintenance headaches.
How to Overcome:
- Invest in Training: Upskill team members through workshops, certifications, and mentorship.
- Hire Experienced Resources: When possible, recruit experienced automation engineers who bring best practices and architectural expertise.
- Promote Knowledge Sharing: Encourage a culture of learning—internal training, code reviews, and knowledge base creation strengthen automation competence.
4. High Initial Investment Costs
Challenge: Automation requires substantial upfront investment—framework design, tool licensing (for paid tools), and infrastructure setup can strain budgets.
How to Overcome:
- Prioritize High ROI Areas: Start automation with high-impact, repetitive, and business-critical test cases to demonstrate value early.
- Balance Open Source and Paid Tools: Weigh the total cost of ownership—including setup, support, and learning curve—when opting for open-source versus commercial tools.
- Phased Implementation: Gradually scale your automation efforts to spread costs over time while building internal capability.
5. Challenges Scaling Test Environments
Challenge: Manual provisioning or limited in-house (on-premise) test environments restricts parallel test execution, slows feedback, and limits automation’s effectiveness.
How to Overcome:
- Adopt Cloud-Based Test Environments: Move to cloud infrastructure to rapidly provision, scale, and tear down environments as needed, enabling greater test coverage and concurrency.
- Embrace Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Use IaC tools for automatic and repeatable environment setup that supports continuous testing.
- Optimize Cost and Scalability: Cloud environments allow you to scale testing efficiently while controlling operational expenses.
By proactively addressing these challenges with the right strategies—strong collaboration, careful tool selection, investment in talent, phased spending, and leveraging the cloud—enterprises can fully realize the benefits of test automation. With the right foundation, automation accelerates software releases, improves quality, and creates a robust, scalable QA process.
Automation Testing Vs Unit Testing
| Criteria | Automation Testing | Unit Testing |
| Definition | Automation tools and scripts are used to execute test cases without manual intervention. | It is a type of testing wherein individual units or software components are tested in isolation. |
| Purpose | Increase efficiency, speed, and coverage of the testing process. Especially beneficial for regression testing. | Validate that each unit of the software functions as designed. |
| Tools | Popular tools include Selenium, QTP, TestComplete, and Cucumber. They cater to various platforms and programming languages. | JUnit (for Java), NUnit (for . NET), and PHPUnit (for PHP) are widely used frameworks. |
| Execution Time | Faster than manual tests once set up. Initial setup might take time. | Quick to write and execute, providing immediate feedback. |
| Scope | It can be used for different levels of testing, including unit, integration, and system testing. | It is |
Why Should You Leverage Next-gen Testing Services Provider for Test Automation?
Test automation is nowadays dominating in the Agile and DevOps adoptions. Test automation enables tremendous benefits to enterprises as it ensures faster releases, quality software and also delivers a quicker time to market.
But, in order to achieve successful test automation for all critical projects, it is essential to leverage next-gen qa automation testing services company as they use a balanced test automation approach to achieve quality products.
Some of the Highlights of the Approach they perform are:
- Assessment of your automation needs and application landscape
- Assessment of your existing automation solution
- Tool selection, Proof of Concept and implementation
- Automated test script creation and execution
- Creation of regression test suites with flexible execution options
- Training and handover of automation test pack to client for future maintenance
Moreover, with the huge number of benefits with automation testing services, it is time for enterprises to adopt test automation initiatives using either open source or the licensed automation testing tools.
TestingXperts has developed an extensible test automation framework, ‘Tx-Automate’, which is modular, reusable, integrated and compatible.
The framework has best-in-class features for test automation including rich custom reporting metrics, third party integrations, configurable execution options, etc.
The framework helps configure/ create test suites by combining various automated tests and making those test suites available for execution.
Get in touch with our team to discuss further
FAQs
Test automation involves using specialized tools to execute test cases, compare actual outcomes with expected results, and streamline repetitive testing tasks. It enhances efficiency, reduces manual effort, and ensures consistency, making it a critical component of modern QA strategies.
Test automation improves testing accuracy, accelerates release cycles, and enhances software quality by detecting defects early. It minimizes human error, increases test coverage, and supports Agile and DevOps practices.
Automated testing ensures faster feedback, improves test coverage, and reduces costs in the long run. It enables continuous testing in CI/CD pipelines, supports parallel execution across devices and platforms, and enhances product reliability.
Popular test automation tools include Selenium, Appium, Cypress, TestComplete, and Playwright. Each tool serves specific testing needs, such as web, mobile, or API testing.
Automation testing meaning can be broadly defined as the process which involves running scripts that are executed by leveraging software testing tools. Automated test systems ensure high accuracy and reliability of the test results.
Test automation improves software quality, speeds up testing, and reduces manual effort. It ensures faster releases and higher efficiency in Agile and DevOps environments.
Key Benefits of Test Automation:
Faster Testing Cycles – Runs tests quickly, accelerating software delivery.
Improved Accuracy – Eliminates human errors for reliable test results.
Cost Efficiency – Reduces long-term testing costs by minimizing manual efforts.
Better Test Coverage – Automates complex test scenarios across multiple platforms.
Test automation helps businesses deliver high-quality, secure, and scalable applications efficiently.
Discover more