Recommended Blogs
Test Automation Frameworks – Why, Types, Benefits, Approach
Table Of Content
- What is Test Automation Framework?
- Why do we use automation framework in test automation?
- What Is the purpose of a Test Automation Framework?
- What is the need for Test Automation Framework for enterprises?
- Different Types of Framework used in Automation Testing
- What are the major advantages of Automation Frameworks for Enterprises?
- What are the steps for an effective Test Automation Approach?
- What Is Selenium Automation Framework?
- What are the types of tests to test automation frameworks?
- Is there an intelligent and easy-to-use Test Automation Framework?
- Why Should Enterprises Leverage Tx-Automate framework?
- Conclusion
Software testing plays a crucial role in the software development lifecycle (SDLC), ensuring applications meet quality standards before release. Traditionally, manual testing was the mainstay of quality assurance. However, with the rise of Agile and DevOps methodologies, along with the growing demand for faster release cycles and higher-quality products, manual testing alone no longer suffices.
This shift highlights the importance of test automation and the frameworks that enable it. Test automation frameworks provide the structured architecture and guidelines for designing, executing, and managing automated test scripts efficiently and reliably. They accelerate testing processes, reduce human error, improve test coverage, and integrate seamlessly into modern development workflows.
In this blog, we’ll explore why test automation frameworks are vital, the various types commonly used, their benefits, and the best approaches to implement them effectively in your software testing strategy.
What is Test Automation Framework?
A Test Automation Framework is a structured set of guidelines, rules, and best practices designed to create, organize, and execute automated test cases efficiently. It serves as a conceptual platform that integrates processes, tools, and protocols to support the automation of software testing activities.
At its core, a test automation framework provides a systematic environment that allows testers to develop reusable automated test scripts, identify application objects, perform actions on them, and evaluate their behavior to verify expected outcomes. By standardizing these activities, the framework enhances resource utilization, improves test reliability, and simplifies maintenance.
More broadly, an automation framework combines hardware, software resources, and automation tools under a qualified set of assumptions and design principles. This integration facilitates effective test script development and supports precise defect identification and analysis for the system or application under test (AUT).
In essence, a test automation framework is the foundation for an automated testing process—a controlled execution environment that ensures consistency, repeatability, and quality in software testing efforts.
Why Do We Use Automation Frameworks in Test Automation?
Automation frameworks are crucial in test automation because they provide a structured and standardized environment that enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of automated testing efforts. Here are the key reasons why frameworks are used:
- Improved Efficiency and Speed: Frameworks streamline the creation, execution, and management of automated tests, enabling teams to run tests faster and more frequently — critical in Agile and DevOps pipelines.
- Increased Test Accuracy and Reliability: By enforcing consistent practices, frameworks reduce human errors and improve the reliability of test results, ensuring defects are detected with higher precision.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Automated test scripts developed within a framework are more modular and reusable. This makes updating and maintaining tests easier and less costly, especially as the application evolves.
- Lower Risk of Test Failures: Frameworks help manage complexities such as handling environment changes, data setup, and reporting, which minimizes flaky or false test failures.
- Supports Scalability and Collaboration: Frameworks provide clear guidelines and reusable components, allowing distributed teams to collaborate smoothly and scale their automation efforts efficiently.
- Integration with CI/CD and Tools: Well-designed frameworks can be easily integrated with continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD) pipelines and other DevOps tools, enabling automated, seamless quality assurance.
In summary, automation frameworks form the backbone of effective automated testing by boosting productivity, ensuring consistent and accurate testing, and supporting sustainable test maintenance — all of which are indispensable in today’s fast-paced software delivery environments.
What Is the Purpose of a Test Automation Framework?
A test automation framework provides a structured approach to designing and executing automated tests. It improves efficiency, consistency, and reliability, helping teams deliver high-quality software faster with less manual effort.
- Enhance Efficiency and Reusability: It streamlines the design and development of automated test scripts by promoting reuse of code and components, reducing duplication and speeding up test creation.
- Provide Structured and Uniform Methodology: By enforcing a standardized approach to test design, the framework ensures consistency across multiple test scripts, minimizing dependency on individual or ad-hoc test cases.
- Enable Reliable Issue Detection and Analysis: The framework facilitates accurate identification of bugs and delivers root-cause analysis with minimal human intervention, improving defect tracking and resolution for the system under test.
- Reduce Team Dependency via Automation Intelligence: It can automatically select and execute appropriate tests based on defined scenarios, reducing reliance on manual decision-making and enhancing automation coverage.
- Support Dynamic Test Scope Adjustment: The framework adapts the scope of testing dynamically according to evolving test strategies or changes in system conditions, ensuring relevant and efficient test execution.
- Optimize Resource Utilization: By organizing and managing resources effectively, it maximizes returns on testing efforts, making best use of available tools, environments, and human expertise.
- Ensure Continuous, Reliable Automated Testing: The framework helps maintain an uninterrupted automated testing process with minimal manual involvement, enabling faster, frequent, and reliable test runs aligned with agile and DevOps practices.
What Is the Need for Test Automation Framework for Enterprises?
Enterprises today operate in fast-paced, competitive environments where delivering high-quality software quickly is critical. Test automation frameworks provide the essential structure and guidelines that enable organizations to design, develop, and execute automated test cases efficiently and consistently at scale.
Key reasons why enterprises need test automation frameworks include:
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Frameworks help testers use resources more effectively by providing reusable components, standardized processes, and organized test suites that reduce duplication and manual effort.
- Consistency Across Teams: By enforcing uniform test design and execution standards, frameworks ensure that automation practices remain consistent across different teams and projects. This uniformity leads to reliable and maintainable test automation assets, improving overall test quality.
- Faster and More Reliable Testing: Well-implemented automation frameworks support rigorous functional and regression testing with shorter test design and execution times. This accelerates feedback loops and enhances defect detection accuracy, enabling enterprises to release high-quality applications faster.
- Scalability to Cover Complex Business Scenarios: Enterprises often face diverse and large application portfolios with complex workflows. Automation frameworks allow combining multiple automated tests into manageable suites, facilitating end-to-end coverage of varied business scenarios.
- Cost and Risk Management: By reducing manual intervention, minimizing redundant efforts, and enabling early defect detection, frameworks help enterprises lower testing costs and risks associated with late-stage failures or production issues.
- Maximizing ROI on Automation Investments: Implementing the right automation framework increases test execution speed and accuracy, ensuring that automation efforts translate into tangible business benefits: faster time-to-market, improved product quality, and reduced maintenance overhead.
- Seamless Integration with Agile/DevOps: Frameworks align well with continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines, supporting automated test execution in modern development workflows common in enterprises.
In summary, test automation frameworks are vital for enterprises to effectively manage their automation efforts, ensuring efficient use of resources, improved test quality, faster releases, and ultimately, delivering superior software products that meet business and user expectations. Selecting and implementing the right automation framework tailored to organizational needs is key to maximizing these benefits.
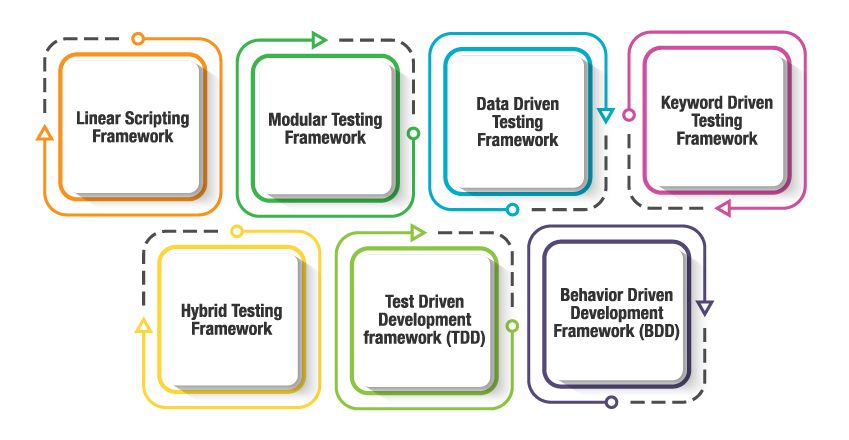
Different Types of Frameworks Used in Automation Testing
Automation testing frameworks have evolved to suit various project needs, test complexity, and team skills. Below are some important types:
1. Linear Scripting Framework
- Also known as the “record and playback” model.
- Scripts are created and executed sequentially in a linear manner.
- Easy to start with and ideal for small projects, but lacks modularity and reusability.
2. Modular Testing Framework
- Based on the concept of “abstraction.”
- Tests are broken down into independent modules; scripts are created for individual units.
- Changes in one part of the application do not impact others, making maintenance easier.
3. Data Driven Testing Framework
- Test data and expected results are stored separately in files (usually tabular, e.g., Excel).
- A single driver script runs test cases repeatedly with different data sets.
- Reduces code duplication and supports wide test coverage with varied input scenarios.
4. Keyword Driven Testing Framework
- Uses keywords and data tables to specify actions and inputs.
- Highly application-independent; extends the data-driven approach.
- Testers can define actions as “keywords,” which increases reusability and clarity.
5. Hybrid Testing Framework
- Combines features of modular, data-driven, and keyword-driven frameworks.
- Offers flexibility, scalability, and reusability by blending various approaches.
- Suitable for complex projects with diverse testing requirements.
6. Test Driven Development Framework (TDD)
- Development is guided by writing automated unit tests before actual code.
- Each new feature starts by defining a test, then code is written/refactored to pass the test.
- Speeds up testing and builds confidence that the system works as expected.
7. Behavior Driven Development Framework (BDD)
- Evolved from TDD, with a focus on expected system behavior.
- Test cases are written in plain English, accessible to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Enhances collaboration between developers, testers, and business analysts.
In summary: Each type of automation framework brings distinct benefits and is chosen based on project complexity, team expertise, and desired outcomes. Understanding these frameworks helps teams pick the right structure for effective, scalable, and maintainable automated testing.
What Are the Major Advantages of Automation Frameworks for Enterprises?
Automation frameworks offer enterprises a strategic edge by streamlining testing processes and driving consistent, high-quality results. They enable efficient reuse of test scripts, accelerate release cycles, and ensure reliable application performance with reduced manual effort. Leveraging these frameworks helps organizations achieve greater scalability, lower costs, and improved product quality in today’s fast-paced development landscape.
Cost-Effective Benefits –
- Reduces Time-to-Market: Automation frameworks enable continuous execution of automated test scripts, helping enterprises accelerate testing cycles and release faster.
- Enhanced Scalability: These frameworks support scaling test coverage as applications grow, accommodating larger test suites and multiple platforms efficiently.
- Lower Operational Costs: Though initial setup costs may be high, automation frameworks reduce long-term operational expenses by minimizing manual testing effort and maintenance overhead.
- Faster, High-Quality Product Launches: Automation ensures consistent test execution, helping deliver reliable and high-quality applications quickly.
- Superior Test Performance Over Manual Testing: Automated tests run with greater speed and accuracy, detecting defects that manual testing might miss.
- Reusable Test Scripts: Test scripts developed within frameworks are reusable for similar testing needs in the future—maximizing return on investment.
- Comprehensive Defect Management: Detailed defect reports generated from automated tests help effectively track and manage quality issues.
Application-Efficiency Benefits –
- Early Defect Identification: Automation frameworks enable faster and more reliable bug detection, allowing teams to address defects early in the development cycle.
- Maximum Test Coverage: End-to-end automated testing ensures all aspects of the application are validated thoroughly across different scenarios.
- Reduced Manual Effort: Fully automated testing minimizes the need for human intervention, freeing up QA resources for higher-level tasks.
- Code Reusability: Reusable test modules improve efficiency and reduce duplication of effort across multiple test cycles.
- Greater Testing Efficiency: Automated test execution significantly reduces testing time, enabling faster feedback and shorter release cycles.
- Anytime, Anywhere Test Runs: Automated scripts can be scheduled or triggered to run at any time, supporting continuous testing in distributed teams.
- Comprehensive Bug Tracking and Reporting: Automation frameworks generate detailed reports that help DevOps and QA teams track issues effectively and integrate feedback into continuous development.
- Crucial for Agile, DevOps, and Continuous Deployment: Automated test frameworks are fundamental enablers of continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, ensuring ongoing quality assurance aligned with modern development practices.
Summary: Automation frameworks empower enterprises to reduce costs, increase scalability, accelerate delivery, and improve product quality by enabling efficient, reusable, and continuous automated testing aligned to Agile and DevOps methodologies.
What Are the Advantages Enterprises Get with Cloud Test Automation Frameworks?
- Delivers Real-Time Communication – Cloud-based frameworks enable seamless, real-time collaboration among distributed development and QA teams. Stakeholders can monitor test progress, access results instantly, and communicate efficiently from anywhere in the world.
- Anytime/Anywhere Access to Data and Resources – Teams can access test environments, data, scripts, and reports 24/7 from any location, removing dependence on local infrastructure and making remote work and global collaboration effortless.
- Supports Parallel Testing Across Platforms, OS, and Environments – Cloud infrastructure allows multiple tests to run simultaneously across a broad spectrum of devices, operating systems, and browsers. This parallelization streamlines cross-platform compatibility testing and uncovers issues faster.
- No Upfront Hardware/Infrastructure Costs – There’s no need to invest in or maintain expensive physical devices, servers, or on-premise test labs. Most cloud solutions follow a pay-as-you-go model, drastically lowering capital expenditure and reducing ongoing maintenance overhead.
- Ensures Faster Time to Market – Rapid setup, instantaneous environment provisioning, and on-demand scalability mean testing cycles are much shorter, enabling quicker releases and keeping pace with Agile and DevOps delivery requirements.
- Delivers Cost Effectiveness – Cloud automation saves costs not only by replacing hardware but also by reducing manual intervention, minimizing downtime, and scaling test resources according to project demand. This leads to improved ROI and operational efficiency
In summary, cloud test automation frameworks empower enterprises with flexibility, speed, and scalability—helping them reduce costs, enhance collaboration, and deliver high-quality software faster in an increasingly competitive digital environment.
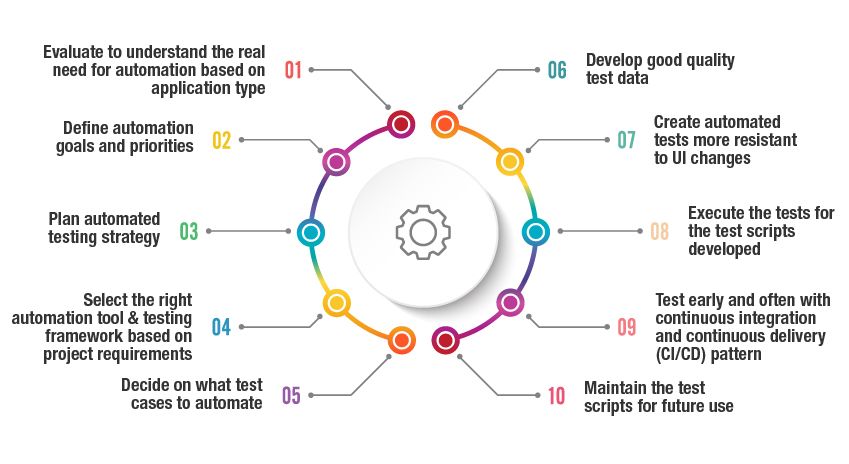
What Are the Steps for an Effective Test Automation Approach?
A well-structured test automation approach is crucial for ensuring software quality and accelerating delivery cycles. By following a systematic process, teams can maximize automation benefits, focus efforts on high-impact areas, and align testing activities with business objectives. The steps below outline key actions for implementing effective and sustainable test automation.
Steps for an Effective Test Automation Approach:
- Evaluate the Need for Automation – Understand the application type, complexity, and suitability to determine if automation will bring value and what parts should be automated.
- Define Automation Goals and Priorities – Set clear objectives for what automation should achieve—such as reducing regression time, improving coverage, or enhancing test reliability—and prioritize accordingly.
- Plan the Automated Testing Strategy – Outline the scope, timelines, resources, and methods for automation, including deciding how automation fits into the overall testing lifecycle.
- Select the Right Frameworks and Tools – Choose test automation frameworks and tools that align with the project’s technology stack, team skills, and testing requirements.
- Decide on Test Cases to Automate – Identify which test cases offer the highest ROI for automation, focusing on repetitive, stable, and high-risk test scenarios.
- Develop Quality Test Data – Prepare reliable, comprehensive test data to cover varied inputs and edge cases that support effective automated testing.
- Create Robust Automated Tests – Design tests that are resilient to UI changes and reduce fragility, using best practices like modular scripting and handling dynamic elements.
- Execute Automated Tests – Run the automated test suites regularly to validate software functionality and catch defects early.
- Integrate Continuous Testing with CI/CD – Implement continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines to test early and often, ensuring rapid feedback and faster releases.
- Maintain and Update Test Scripts – Regularly review and update test scripts to accommodate application changes, optimize performance, and ensure long-term automation effectiveness.
Following these steps ensures a systematic, efficient, and scalable approach to test automation that aligns with business goals and accelerates software delivery.
What Is Selenium Automation Framework?
Selenium is a leading, portable test automation framework widely used for testing web applications. It allows testers to automate interactions with browsers and verify application behavior across multiple environments. One of Selenium’s notable features is its record and playback capability, enabling users to create and author functional tests without extensive programming knowledge. This feature simplifies test creation and accelerates automation processes, especially for teams new to automated testing.
Testers also leverage various other frameworks—such as integration testing frameworks, UI testing frameworks, and keyword-driven frameworks—to enhance their automation strategies. The choice of framework depends on the type of application under test and the specific testing requirements. Selecting the most suitable framework ensures comprehensive test coverage and maximizes the benefits of automation.
What Are the Types of Tests to Test Automation Frameworks?
Before adopting a test automation framework, it’s crucial to evaluate it thoroughly. Conducting a variety of tests ensures the framework’s quality, reliability, and suitability for your team and project needs. Here are key types of tests to consider:
- Functional Testing: Verifies that the framework’s core features—such as test execution, reporting, integration, and result logging—operate as intended.
- Learning Tests: Assesses how quickly new users can understand and start using the framework, testing its intuitiveness and learning curve.
- Upgradability Testing: Ensures the framework can be smoothly upgraded as new versions are released without breaking existing test scripts or integrations.
- Installability Testing: Checks how easy it is to install and configure the framework on different systems and environments.
- Portability Testing: Evaluates whether the framework can be used across different operating systems, environments, or platforms without significant issues.
- Interoperability Testing: Tests the framework’s ability to integrate and work with other tools, such as CI/CD platforms, libraries, and cloud services.
- Performance Testing: Measures the speed and efficiency with which the framework executes large numbers of automated tests, identifying potential bottlenecks or scalability issues.
- Suitability Testing: Determines if the framework aligns with your technical requirements, project needs, and preferred programming languages.
- Syntax Testing: Ensures that the framework’s scripting syntax is consistent, clear, and free from ambiguous or conflicting commands.
- Usability Testing: Focuses on the user experience, evaluating the interface, documentation, error messages, and overall ease of use for testers.
- Understandability Testing & Static Analysis: Reviews the clarity of documentation, code quality, and maintainability of the framework, ensuring that it can be effectively used and extended by different team members.
Conducting these tests helps ensure that your chosen test automation framework will be robust, maintainable, and a good fit for your team, ultimately leading to more efficient and reliable automated testing processes.
Is There an Intelligent and Easy-to-Use Test Automation Framework?
Tx-Automate – An Intelligent and Ready-to-Deploy Test Automation Framework
Tx-Automate is an innovative, extensible test automation framework designed for reusability, rapid deployment, and comprehensive compatibility. Its main highlights include:
Framework Overview (Tx-Automate)
- Matured Continuous Integration/ Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) solution across a diverse set of applications (Digital, IoT, API, Legacy and more)
- Best-in-class features for test
- Rich custom reporting & configurable execution options
- Supports integration with market-leading test automation framework open source and commercial tools
- Supports functional and non-functional tests within an automated pipeline
Core Framework Features:
- Matured CI/CD Solution: Supports continuous integration and delivery across a wide set of application types—Digital, IoT, APIs, Legacy, and more.
- Best-in-Class Automation Features: Includes rich custom reporting, configurable execution options, and seamless integration with both open-source and commercial testing tools.
- Integrated Pipeline Support: Capable of managing functional and non-functional (performance, security) tests efficiently within an automated testing pipeline.
- Flexible Test Suite Configuration: Easily configure, combine, and execute various automated test suites for end-to-end testing coverage.
- Out-of-the-Box Readiness: Helps teams drastically reduce setup effort and quickly kick-start automation initiatives.
Key Advantages:
- Tool Agnostic: Integrates with popular testing tools such as Selenium, Appium, and supports a wide range of open-source and commercial solutions.
- Rich Reporting: Generates detailed UI-based output reports tailored for different stakeholders, including test status, results, and defect analysis.
- CI/CD and Third-Party Integration: Offers seamless integration with CI/CD tools (like Jenkins), test management, version control, and bug-tracking tools.
- Cloud Support: Interfaces with cloud providers for on-cloud test execution, increasing flexibility and parallelism.
- Reusable Components: Includes a library of reusable code components, driver scripts, and configuration files, making maintenance and script creation easier.
- Object Identification: Utilizes the Page Object Model for robust and scalable object identification.
- Command-Line Execution and Notifications: Supports command-line test execution and multiple notification formats to keep teams updated.
Why Should Enterprises Use Tx-Automate?
- Plug-&-Play Flexibility: Designed for minimal setup—easy to deploy and adapt to changing business and technology needs.
- Wide Technology and Language Support: Integrates with the latest technologies and many programming languages; supports cross-browser testing and alternate frameworks.
- Scalability and Maintenance: Manages large script repositories in real time and is straightforward to update or expand.
- Ideal for Modern Quality Practices: Fits agile, DevOps, and cloud-native workflows, making it highly relevant in today’s fast-paced development environments.
Tx-Automate enables enterprises to accelerate test automation adoption, improve quality, scale efficiently, and seamlessly integrate testing into continuous delivery pipelines—not only boosting overall test coverage but also optimizing cost and time-to-market.
Conclusion
As agile and DevOps practices shape modern software delivery, the pressure for faster releases and higher product quality intensifies. Test automation frameworks play a pivotal role by enabling quicker defect detection, reusable scripts, and reduced manual intervention, all of which support rapid, reliable deployments. To maximize these benefits, enterprises should consider partnering with independent next-gen software testing service providers who offer robust, plug-and-play automation frameworks—making it easier to achieve continuous, high-quality releases at scale.
FAQs
-
It consists of a set of processes, tools, and protocols that can be collectively used for automated testing of software applications.
-
There are seven types of automation testing frameworks: Linear Scripting Framework, Modular Testing Framework, Data-Driven Testing Framework, Keyword-Driven Testing Framework, Hybrid Testing Framework, Test-Driven Development (TDD), and Behavior-Driven Development (BDD).
-
An automation testing framework is a platform developed by integrating various hardware, software resources along with using various tools for automation testing and services based on a qualified set of assumptions.
-
Selenium is a leading test automation framework that is portable and is used for testing web applications. Selenium test automation services provides a record and playback feature for authoring functional tests.
Discover more
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info